Classical Approach to Output and Price Determination:
Among economists there is no agreement on how adjustments in equilibrium levels of output, prices and employment take place. There are also differences in views oil the sources of economic fluctuations. Basically there are two important schools of thought: classical and Keynesian. Classical approach is a term coined by John Maynard keynes to reflect the ideas presented by economists prior to him. Prominent among classical economists Adam Smith, David Ricardo, Thomas Malthus and John Stuart Mill. The classical and Keynesian economists differ on:
i) the relative roles played by supply and demand in determination of output, employment and prices,
ii) the flexibility of prices and wage rate in the economy, and
iii) the dichotomy between real sector and monetary sector.
The mainstay of classical economics has been the basic assumption that 'supply creates its own demand; often referred to as 'Say's law', named after J. B. Say. The Keynesian economists rule out such a possibility, particularly during periods of recession.
The classical economists believed in free trade and minimum intervertion by thle government on economic activities. They suggested a 'laissez-faire' (French for 'leave us alone') economy where government should confine itself to law, defence and
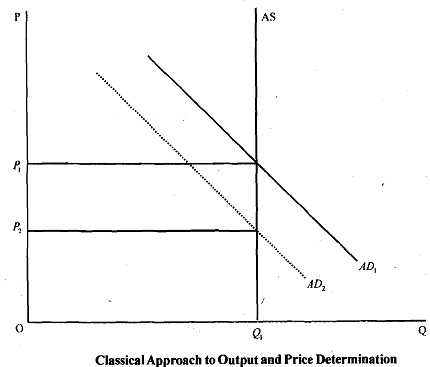
governance. In such an economy 'market forces' will determine real variables such as output, employment and prices. This is made possible by flexibility in price and wage levels. The classical economists believed that the aggregate supply curve is vertical, so that there is no change in equilibrium level of output and employment.
For example, suppose there is a downward shift in aggregate demand from AD1 to AD2, due to reduced consemptin expenditure by households. This will result in excess supply at the prevailing price P1. Consequently, prices will decline to P2 while there will be n$ decline in output level, and market gets cleared. In the factor market, wage rate will decline so that lll employment is maintained. According to classical economists there iS a 'self-correcting mechanism behind the 'market clearing model of the economy. The process of change in wage rate and prices are achieved instantaneously. The classic economists also assume dichotomy between real variables (such as output and employment) and nominal variables (such as money supply and prices). Thus changes irb money supply (M) do not influence output or employment. If there is a decrease in money supply, levels of prices and wage rate will decline.
The Keynesian approach, however, does not subscribe to the vertical AS curve. Keynes points out that in the short run there are price and wage 'rigidities' so that prices and wage rate do not decline when there is a downward shift in aggregate demand. Wag rigidities arise because of various contracts and labour legislation. Due to wage rigidity, wage rate is maintained at a higher level, Consequently, the output level declines and there is 'recession' in the economy. In the short-run the AS curve is either horizontal ot upward sloping (in Fig. we have presented an upward sloping AS curve so that downward shift in AD results in decline in both output and price levels). In the Keynesim model, however, the AS curve is assumed to be vertical in the long run so that output supplied is fixed. Thus we can say that the classical model explains the long run while the Keynesian model explains the short run.
In response to the Keynesian economics the 'neoclassical economists' (John Hicks, Paul Sarnuelson, Robert Solow among others) attempted to imbibe the important ideas of Keynesian economics in a classical framework. The pioneering efforts by Sir John Hicks paved the way for the synthesis of classical and Keynesian ideas on real and nominal macro-variables, popdarly known as IS-LM model. The neoclassical growth model by Solow helped in analysis of long run growth of an economy. The 'new classical economics' is a term broadly used to describe the challenges posed to the Keynesian orthodoxy. This school of thought suggests that economic fluctuations can be explained while maintainjng classical assumptions.