Aggregate Demand:
In macroeconomics we use the term aggregate demand (AD) to include the total demand for goods and services produced in the economy. Aggregate demand is an inverse function in prices depicted by a downward sloping curve. Thus, as prices increase, aggregate demand decreases.
Aggregate demand is viewed in terms of expenditure or spending on goods and services. There are four major components of aggregate deniand:
i) consumption expenditure,
ii) investment,
iii) goverment expenditure, and
iv) net exports. Thus
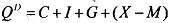
where QD is aggregate demand, C is consumption expenditure, I is investment, G is government expenditure, X is exports and M is imports. Thus (X-M) indicate net exports. In a closed economy, where there is no foreign trade, X and M are equal to zero.