WALLS
Walls are built to partition living area into different parts. They impart protection against temperature, rain and theft and privacy. Walls may be classified as
- Load bearing walls
- Partition walls.
1. Load Bearing Walls: If columns and beams are not used, load from floors and roof is transferred to foundation by walls. Such walls are known as load bearing walls. To transfer the load safely they are to be designed. The critical portion of the walls are near the openings of windows and doors and the positions where concrete beams rest.
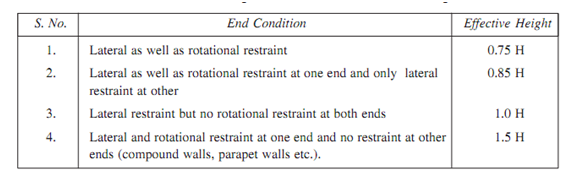
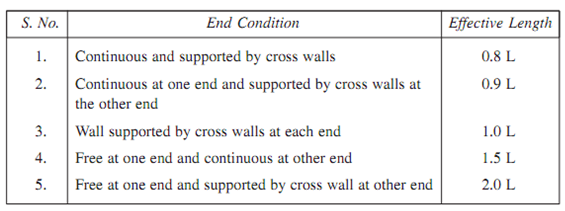
Minimum wall thickness used is 200 mm. This is also recommended that the slenderness ratio of wall defined as ratio of effective height or effective length to thickness might not be more than 27. The effective length and effective height of a wall may be taken as shown in given table respectively.
Effective height of walls in terms of actual height H
Effective length of walls of length L
2. Partition Walls: In framed structures for different utilities partition walls are built to divide floor area. They rest on floors. From floor and roof they do not carry loads. They have to carry only self-weight. Therefore normally partition walls are thin. Given figure shows differences between partition walls and load bearing walls .These walls may be brick partition, wood partition, clay block partition, glass partition, and aluminium and glass partition depending upon the requirement.
Differences between load bearing and partition walls
