SCALES
It is not possible and also not wanted to make maps to one to one scale. By a fixed proportion whereas making maps all distances are reduced. That fixed proportion is called scale of the map. So, if 1 mm on the paper represents 1 metre on the ground then the scale of the map is 1 mm = 1 m or 1 mm =1000 mm or 1: 1000. it is preferable to use representative factor to make scale independent of the units which may be defined as the ratio of one unit on paper to the number of units it represent on the ground.
Thus 1 mm = 1 m is equivalent to
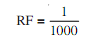
It is desirable to show it graphically apart from writing scale on map, on it. The reason for it is, over the time, the paper may shrink and the scaling down the distances from map can mislead. The graphical scale should be adequately long (180 mm to 270 mm) and the main scale divisions should represent one, ten or hundred units so that it can be read easily.
The scale of a map is considered as
(i) large if it is greater than 1 cm = 10 m for example,
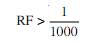
(ii) Intermediate if it is between
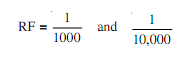
(i) small if
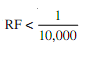
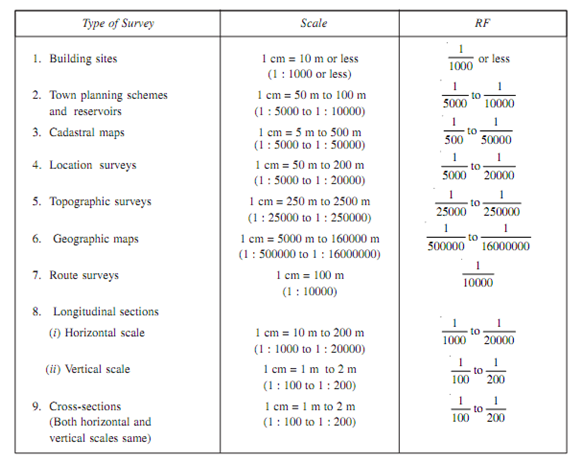
Generally, since for human eye it is not possible to distinguish among two point if distance between them is less than 0.25 mm scale selected should be as large as possible,. The recommended scales for different types of surveys are as shown in Given Table.
Table: Recommended scales for various types of surveys