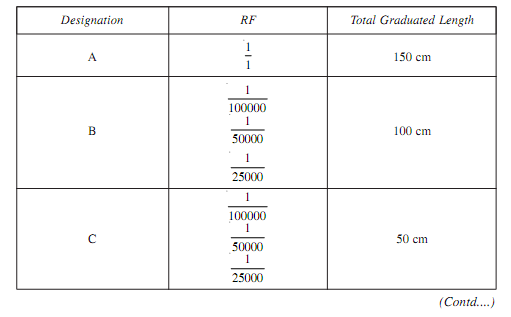
Plain Scale
It is possible to read two dimensions directly such as unit and tenths on a plain scale. This scale is not drawn as ordinary foot rule (30 cm scale)., the markings are not as 8 m, 4 m 12 m etc. at every 1 cm distance If a scale of 1: 40 is to be drawn. Construction of such type of scale is illustrated with the instance given below:
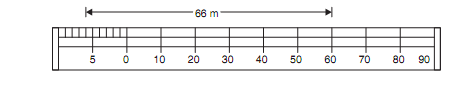
Example : Construct a plain scale of RF =1/500 and show 66 m on it.
Solution. If the total length of the scale is let as 20 cm, it represents a total length of 500 × 20 =10000 cm = 100 m. therefore, draw a line of 20 cm and divide it into 10 equal parts.
Therefore, each part corresponds to 10 m on the ground. On extreme left first part is subdivided into 10 parts, each subdivision on the field representing 1 m. Then they are numbered as 1 to 10 from right to left as shown in given figure. If on the ground a distance is between 60 and 70 m, by placing one leg on 60 m marking and the other leg on subdivision it is picked up with a divider in the first part. So field distance is converted to map distance easily.
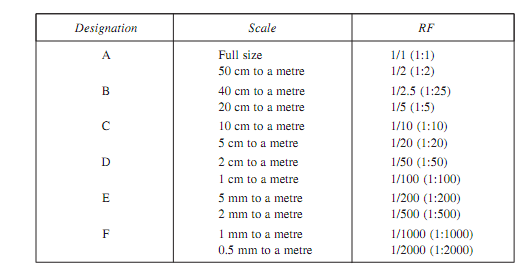
IS 1491-1959 recommends requirements of metric plain scales designated as A, B, C, D, E and F as shown in given table. In the market commonly such scales are available. They are made of either varnished cardboard or of plastic materials. Such type of scales are used by surveyors and architects commonly.
Table Recommended plain scales
In plain scale unit and tenths can be only shown while in diagonal scales it is possible to show, tenths, units and hundredths. In the same manner Units and tenths are shown as in plain scale. Principle of similar triangle is used to show hundredths,. If AB is a small length and its tenths are to be shown, it can be shown as described with given figure below.

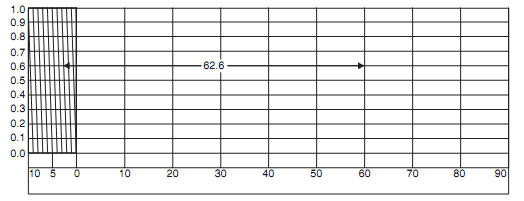
Diagonal scale
IS 1562-1962 advice diagonal scales A, B, C, and D as shown in given table.
Indian standard diagonal scales (recommended)