4-Wire, Three-Phase Wye System:
Till now, the phase voltage, the voltage, and the ground voltage of the three-phase systems have been equivalent, along with the one exception of one phase of the corner-grounded Delta. The Wye system has fully different voltage features from the Delta system. Within the Wye system, the ground voltage or voltage available from phase to ground is the phase voltage divided through 1.73.
Within Figure, an instance of the Wye system, or center-grounded Wye as it is generally referred to, extends three current-carrying insulated conductors and an insulated grounded neutral to the loads. It Depending on the selection of conductors, one of the subsequent is available: a reducedvoltage single phase among a phase leg and the neutral; a full-voltage single-phase circuit among any two phase legs; or a full-voltage three-phase power. Over, a few precautions must be taken while balancing the single-phase loads in the system. A full load ampacity of the neutral must be sized to 1.73 times the highest phase ampacity. This is completed to prevent either an over-current condition if a fault is present or the operation of single-phase loads at reduced voltage if the loads become severely unbalanced through accidental interruption.
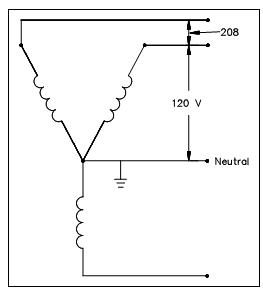
Figure: 4-Wire, Three-Phase Wye System
As along with all other grounded systems, bonds are established among the grounded neutral and all elements of the system. That system is recognized as the safest possible multi-purpose distribution system for low voltage and is generally seen in the 208/120-volt range in several facilities.