Biosynthesis of cholesterol:
Animals are able to synthesize cholesterol de novo through an elegant series of reactions in that all 27 carbon atoms of cholesterol are derived from acetyl CoA. The acetate units are first transformed into C5 isoprene units, which are then condensed to form a linear precursor to the cyclic cholesterol.
The first stage in the synthesis of cholesterol is the creation of isopentenyl pyrophosphate shown in the figure. acetoacetyl CoA and Acetyl CoA combine to form
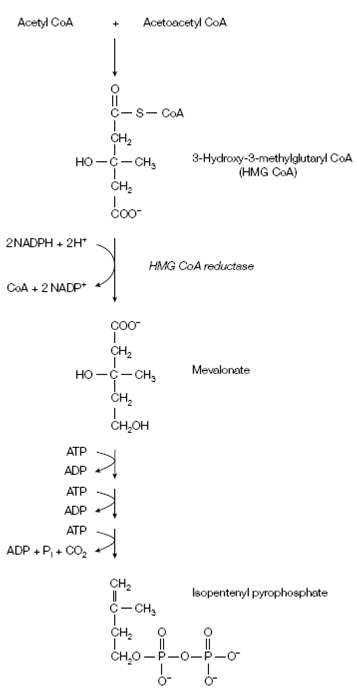
Figure: Synthesis of isopentenyl pyrophosphate.
3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl CoA (HMG CoA). This procedures takes place in the liver, wherever the HMG CoA in the mitochondria is used to establish ketone bodies in during starvation, while which in the cytosol is used to synthesize cholesterol in the fed state (under the influence of cholesterol). An HMG CoA is then decrease to mevalonate through HMG CoA reductase shown in the figure. This is the committed step in cholesterol biosynthesis and is a key control point. Mevalonate is transformed into 3-isopentenyl pyrophosphate through three consecutive reactions each including ATP with CO2 being released in the final reaction shown in the above figure.
The C5 isoprene units in isopentenyl pyrophosphate are then condensed to form the C30 compound squalene shown in the figure. First, isopentenyl pyrophosphate isomerizes to dimethylallyl pyrophosphate described in figure that reacts with another molecule of isopentenyl pyrophosphate to form the C10 compound geranyl pyrophosphate. A different molecule of isopentenyl pyrophosphate then reacts with geranyl pyrophosphate to creation the C15 compound farnesyl pyrophosphate. Then, two molecules of farnesyl pyrophosphate condense to form squalene.
Squalene is then converted into squalene epoxide in a reaction that uses O2 and NADPH described in the figure. The squalene epoxide cyclizes to form lanosterol, and at last cholesterol is create from lanosterol through the removal of three methyl sets, the reduction of one double bond through NADPH and the migration of the other double bond shown in the given figure.
Farnesyl pyrophosphate and the C20 compound geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate (that is created through the condensation of another isopentenyl pyrophosphate with farnesyl pyrophosphate) are covalently associated to cysteine residues in a number of proteins, providing increase to prenylated proteins and promoting their relation with membranes. Dolichol, that holds some 20 isoprene units, is used to hold the biosynthetic precursor of the N-linked oligosaccharides which are subsequently attached to proteins.