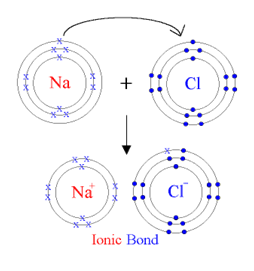
Ionic Bond
The ionic bond occurs between metals and nonmetals. When a metal reacts with a nonmetal, the metal (as it has lower number of outermost shell electrons) loses/donatesits outermost shell electrons to the nonmetal. Thus it completes its outermost shell (octet), and forms a positively charged ion (cation), due to more protons than the total number of electrons.
The nonmetal, on the other hand, gains electrons to complete its outermost shell and forms a negatively charged ion (anion). Attraction between ions of these opposite charges results in the ionic bond.
Properties of ionic compounds:
(i) Composed of ions
(ii) They are solids which are having high melting and boiling points
(iii) Soluble in polar solvents like water but insoluble in non-polar solvents like alcohol, methylbenzene etc.
(iv) Crystalline solids
(v) Non-conductors of electricity in solid state but conducts electricity in aqueous or molten state.
(vi) They are brittle.
(vii) Chemical reactions involving ionic compounds are rapid.