The Atom
1. The basic unit of matter is atom.
2. It is composed of 3 sub-atomic particles, proton, electron, and neutron.
3. The protons and neutrons are found at center of an atom and are constituents of the nucleus.
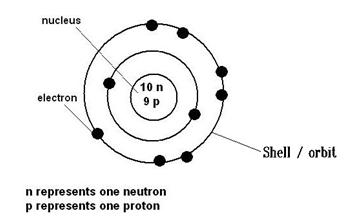
4. The electrons revolve around the nucleus in very high speeds in specific paths called as shells or orbits.
5. The nucleus is very small (if whole atom is the size of a football field the nucleus would be size of a pea), but contains over 99.9% mass of the whole atom.
6. The protons are positively charged in nature and have a relative mass of 1.
7. The electrons are negatively charged in nature and have negligible mass (1/1836).
8. The neutrons have no charge and has a relative mass of 1 (equal to that of a proton).
|
Sub-atomic particle
|
Relative mass
|
Relative charge
|
|
Proton
|
1
|
+1
|
|
Neutron
|
1
|
0
|
|
Electron
|
negligible
|
-1
|
9. An atom is electrically neutral as it has equal number of protons and electrons and so the positive charge of protons cancels out negative charge of electrons and vice-versa.
10. If an atom has unequal number of protons and electrons it will be charged and known an ion.
11. If an atom (generally metals) loses electrons the positive charge of protons will dominate over the negative charge of electrons and ions will be positively charged.
12. Gaining of electrons by atoms (generally non-metals) gives them a negative charge because of greater number of electrons than protons.
13. Atoms have a tendency to gain or lose or share electrons as all atoms want to attain full outermost shell electrons and be stable.
14. Group VIII elements are known as noble gases because they contain full outermost shell electrons and are stable in their unreacted state and so has no tendency to react.
15. The total number of protons in the nucleus of one atom of an element is known as proton number or atomic number.
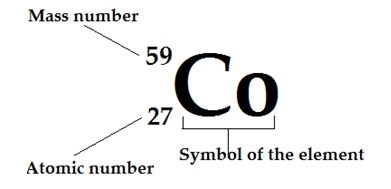
The figure shows a representation of a typical atom. A cobalt atom has 27 protons and has a mass number of 59 (total number of neutrons and protons). So, there should be 32 neutrons
(neutron number = mass number - proton number)
16. The total number of protons and neutrons is called as the mass number or nucleon number.
17. The atomic number or proton number is identity of an atom and determines the chemical element.
18. The diameter of the typical atom is 10-9 m.
19. Isotopes are atoms which are having the same atomic number but different mass number because of different number of neutrons.