Factors Affecting Chemical Shift:
You have learnt that the chemical shift arises due to the two kinds of effects namely the diamagnetic and paramagnetic effects. These in turn arise because of the circulation of the electrons surrounding the nucleus. Thus, any factor which might alter the electron density in the proximity of nucleus (proton) would affect chemical shift. Let us learn about some of these.
Electronegativity: You know that an atom of high electronegativity in a molecule draws electron density towards itself. This causes a reduction within the electron density leading to deshielding of the nucleus. Therefore, with increasing electronegativity δ values will become high or go downfield. Now let us see a few examples as given in Table.
Table: The effect of electronegativity and the number of halogen atoms on the chemical shift position of protons in simple methylhalides
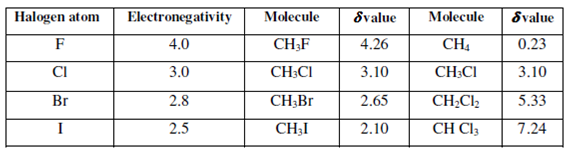
The data shows that the effect of increasing electron withdrawal on the chemical shift of the remaining protons is cumulative but not additive. It may be concluded that with increasing shielding, electronegativity of protons decreases.