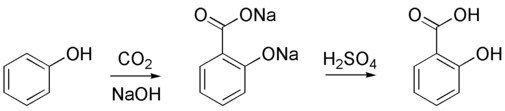
The Kolbe-Schmitt reaction/Kolbe process (named for the Adolph Wilhelm Hermann Kolbe and Rudolf Schmitt) is a carboxylation chemical reaction that follows by heating sodium phenolate (the sodium salt of phenol) with carbon dioxide under pressure (100 atm, 125°C), then treating the product with sulfuric acid. The end product is an aromatic hydroxy acid which is also called as salicylic acid (the precursor to aspirin).
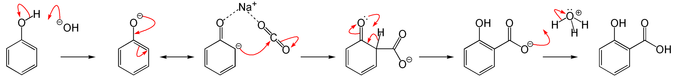
Reaction Mechanism -
Email based Kolbe–Schmitt reaction assignment help - Kolbe–Schmitt reaction homework help at Expertsmind
Are you finding answers for Kolbe–Schmitt reaction based questions? Ask Kolbe–Schmitt reaction questions and get answers from qualified and experienced chemistry tutors anytime from anywhere 24x7. We at www.expertsmind.com offer Kolbe–Schmitt reaction assignment help - Kolbe–Schmitt reaction homework help and Chemical Reactions problem's solution with step by step procedure.
Why Expertsmind for Chemistry assignment help service
- Higher degree holder and experienced tutors
- Punctuality and responsibility of work
- Quality solution with 100% plagiarism free answers
- On Time Delivery
- Privacy of information and details
- Excellence in solving chemistry queries in excels and word format.
- Best tutoring assistance 24x7 hours