Covalent Bonds:
A covalent bond is twisted while one or more electrons from an atom pair off along with one or more electrons from another atom and figure overlapping electron shells in that both atoms share the paired electrons. Dissimilar an ionic bond, a covalent bond contains together specific atoms. Covalent bonding could be double covalent, single covalent, or triple covalent depending on the number of pairs of electrons shared. Below figure displays the bonding which occurs within the methane molecule that consists of four single covalent bonds among one carbon atom and four hydrogen atoms.
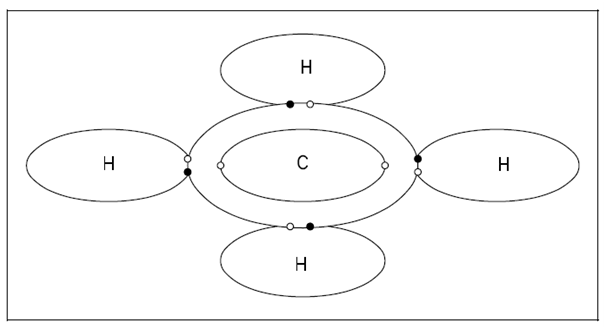
Figure: Covalent Bond, Methane CH4
Two double covalent bonds output while carbon dioxide that consists of one carbon atom and two oxygen atoms is created. Four pairs of electrons are shared through the carbon atom, two from every of the two oxygen atoms as display in Figure. A mixture of two electrons forms a combination of lower energy than their energy while divided. This energy difference represents the force which binds exact atoms together.