Cations:
A positively charged ion is electron deficient and that works as an electrophile. The atom that bears the positive charge is the electrophilic center. In the matter of a carbocation, this is the carbon atom. A number of molecules (for example the allylic cation) are capable to delocalize their positive charge between two or more atoms in which case all the atoms able of sharing the charge are electrophilic centers.
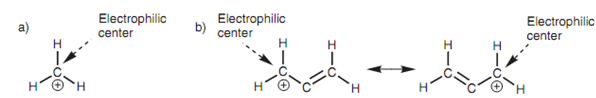
Figure: Examples of electrophiles: (a) carbocation; (b) allylic cation.
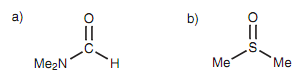
Figure: (a) Dimethylformamide (DMF); (b) dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO).