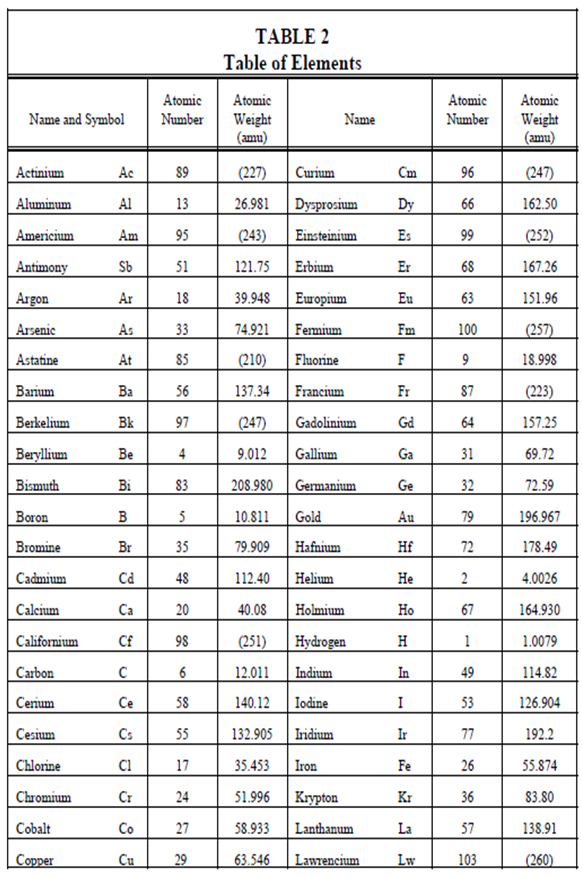
Atomic Weight:
In Table, the masses of atomic particles are provided in atomic mass units (amu). Those units represent an associative scale within that the mass of the isotope carbon-12 is used as the standard and all others are associated to it. Specifically, 1 amu is described as 1/12 the mass of the carbon-12 atom. Because the mass of a proton or a neutron is around 1 amu, the mass of a particular atom will be approximately equivalent to its atomic mass number, Z.
The atomic weight of an element is commonly more meaningful than isotopic masses. An atomic weight of an element is described as the weighted average of the masses of all of its natural occurring isotopes. An atomic weight of the components is listed in Table 2. The components which have their atomic weights within parentheses are unstable. For these components, the atomic weight of the longest living isotope is used quite than the average of the masses of all occurring isotopes.