Atom Structure:
Whole matter is composed of atoms and existing individually or in combination along with another. An atom is a very small electrically-neutral particle. It is the smallest unit included in the chemical change of matter. Atoms could be treated as distinct particles since they behave as such chemically, other than atoms themselves are composed of even smaller subparts. Knowing these atomic subparticles is significant within understanding chemistry.
An atom is composed of a positively-charged nucleus orbited through one or more negatively-charged particles known as electrons. A simplified schematic representation of this arrangement is described in below Figure. The nucleus is the core of an atom. It has a positive charge since it commonly consists of two particles, the neutron and the proton (hydrogen is the exception along with only a proton in the nucleus). The neutrons are electrically neutral, a proton is electrically positive. The nucleus with one proton has a charge of +1 (or simply 1), and a nucleus along with two protons has a +2 charge. Both the neutrons and protons provide the nucleus it's mass, other than the proton alone provides the nucleus its positive charge.
Neutrons and protons are associatively massive and are necessary equivalent in mass.
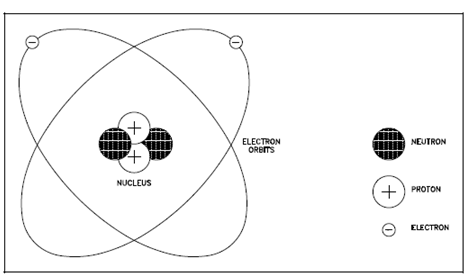
Figure: Schematic of a Simple Atom (Helium)