Differential Velocity Centrifugation
The several subcellular organelles are separated from one another on the behalf of their size in differential velocity centrifugation. A centrifuge is used to produce powerful forces; up to 100 000 times the force of gravity (g). The homogenized sample is placed in an suitable centrifuge tube which is then loaded in the rotor of the centrifuge and subjected to centrifugation. For short periods at first relatively low g forces are used of time but then for longer time periods increasingly higher g forces are used. For instance, centrifugation at 600g for 3 min would pellet the nuclei, the largest organelles .The supernatant from this step is removed to a fresh tube and then for 8 min centrifuged at 6000g to pellet out mitochondria, peroxisomes and, if present, chloroplasts or lysosomes. Centrifugation of this next supernatant for 30 min at 40 000g will pellet out the plasma membrane, and fragments of the Golgi apparatus and endoplasmic reticulum. A final centrifugation for 90 min at 100 000g would result in a ribosomal pellet and a supernatant that is basically free of specific matter and it is considered to be the true soluble cytosolic fraction.
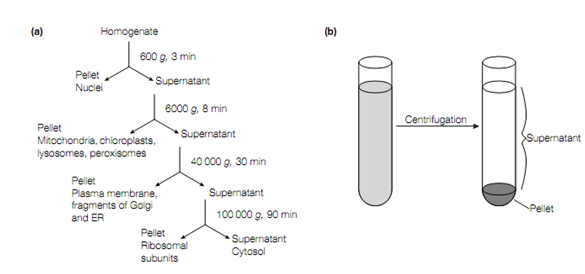
By differential velocity centrifugation Cell fractionation (a) format for subcellular fractionation of a tissue sample, (b) in the centrifuge tube appearance of a sample before and after centrifugation.
On the other hand, by differential velocity centrifugation the fractions isolated are not entirely free of other subcellular organelles usually and so may need to be purified further. A preparative centrifuge is used which has a rotor spinning in air at ambient pressure at low g forces for separations. However, an ultracentrifuge is needed for separations at higher g forces. To reduce friction the chamber of the ultracentrifuge is kept in a high vacuum, and subsequent heating, which would otherwise take place between the spinning rotor and air.