Naphthenic acids:
Naphthenic acid is the name given to a group of cyclic aliphatic monocarboxylic acids having the following general structure:
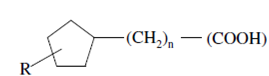
Naphthenic acids
This fraction of crude petroleum has a molecular weight in the range of about 170 - 330.
Aliphatic and aromatic sulphonic acids are represented by the formula RSO2OH (R = straight/ branched chain or aromatic saturated radical). A variety of these extractants are available and more useful of these reagents are dodecylbenzene and dinonylnaphthelene sulphonic acids. Aliphatic sulphuric acids with the general formula ROSO3H (R= alkyl chain usually at least 15 carbon atoms), have been shown to be potentially useful extractants.
Carboxylic, naphthenic and sulphonic acids are associated in organic solvents. This is based on considerations of medium effect on the extent and strength of inter molecular hydrogen bonding in such compounds. The effects of aqueous phase parameters on the extraction of metals are similar in all the different type of acids. The major difference between the sulphonic (and sulphuric) and carboxylic acid extractants is the capacity of the former to extract cations from solutions below pH 1. As a rule, the distribution ratio decreases with increasing acidity.
Dimerization of carboxylic acids in non-polar solvents is well established. The extracted species are invariably solvated by one or more extracted molecules. Carboxylic acids also have a tendency to higher polymerization with increase in concentration of extracted metal. In the extraction of Ni(II), Co(II) and Cu(II) by naphthenic acid, the extracted species have been reported as Ni2. A4. 4HA, Co2A4• 4HA, Cu2A4•4HA, respectively.