Structure and Properties
Structure
Carboxylic acid derivatives are structures that derived from a parent carboxylic acid structure. There are four general kinds of acid derivative. That is
- Acid chlorides,
- Acid anhydrides,
- Esters, and
- Amides.
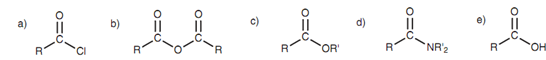
Figure: (a) Acid chloride; (b) acid anhydride; (c) ester; (d) amide; (e) carboxylic acid.
These functional groups contain a carbonyl group (C=O) in which both atoms are sp2 hybridized. The carbonyl group together with the two neighboring atoms is planar with bond angles of 120?.
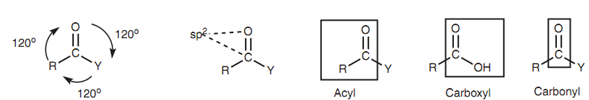
Figure: Structure of the functional group.
The carbonyl group together with the attached carbon chain is termed as an acyl group. Carboxylic acids and carboxylic acid derivatives are different from in what is attached to the acyl group (that is Y = Cl, OCOR, OR, NR2, or OH). Note that in all these cases, the atom in Y that is directly connected to the carbonyl group is a heteroatom (Cl, O, or N). This differentiates carboxylic acids and their derivatives from aldehydes and ketones in which the corresponding atom is hydrogen or carbon. This is significant with respect to the sort of reactions that carboxylic acids and their derivatives go through. The carboxylic acid group (COOH) is frequently considered to like a carboxyl group.