Reactivity:
Reactivity order
Acid chlorides can be transformed to acid esters, anhydrides, or amides. These types of reactions are feasible since acid chlorides are the very much reactive of the four carboxylic acid derivatives. Nucleophilic substitutions of other acid derivatives are much more limited since they are less reactive. For instance, acid anhydrides can be employed to synthesize esters and amides, but cannot be employed to synthesize acid chlorides. The probable nucleophilic reactions for every carboxylic acid derivative depend upon its reactivity with respect to the other acid derivatives as shown in figure. Reactive acid derivatives can be transformed to less reactive (much more stable) acid derivatives, but not another way round. For instance, an ester can be transformed to an amide, but not to an acid anhydride.
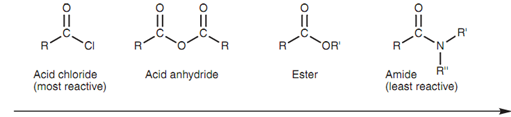
Figure: Relative reactivity of carboxylic acid derivatives.