Enolate Reactions:
Enolates
Enolate ions can be made from aldehydes and ketones consisting of protons on an α-carbon. Enolate ions can as well be made from esters if they have protons on an α-carbon. Such types of protons are slightly acidic and can be eliminated on treatment with a powerful base like lithium diisopropylamide (LDA). LDA works like a base rather than as a nucleophile because it is a bulky molecule and this avoids it attacking the carbonyl group in a nucleophilic substitution reaction.
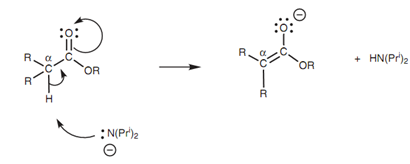
Figure: Enolate ion formation.
Creation of enolate ions is much easier if there are two esters flanking the α-carbon because the α-proton will be more acidic. The acidic proton in diethyl malonate can be removed with a much weaker base as compared to LDA (for example sodium ethoxide). The enolate ion is much more stable because the charge can be delocalized over both carbonyl groups.
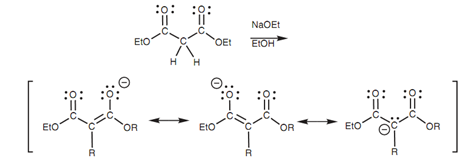
Figure: Formation of an enolate ion from diethyl malonate.