Vectors in the RC plane:
RL impedances can be represented in the form of vectors as well. The same is true for RC impedances.
In the Figure given below, there are 4 different impedance points. Each one is represented by the certain distance to the right of origin (0,0), and the certain displacement downwards. The 1st of these is the resistance, R, and the 2nd is the capacitive reactance, Xc. Thus, the RC impedance is a 2-dimensional quantity.
This look like a mirror image reflection of RL impedances. You could imagine that we are looking at an RL plane reflected in the pool of still water. This is, actually, an excellent way to envision the situation.
The impedance points in RC plane can be rendered as vectors, just as this can be done in RL plane. Then points become rays, each with the certain length and direction. The magnitude and direction for the vector, and coordinates for the point, uniquely define same impedance value. The length of vector is distance of the point from the origin, and direction is the angle measured clockwise from resistance (R) line, and specified in the negative degrees. The equivalent vectors, for points are illustrated in the Figure given below.
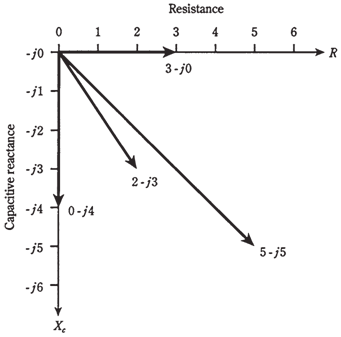
Figure-- Four vectors in the RC impedance plane.