Discharging a Capacitor:
Since very few of the charges could cross among the plates, the capacitor will remain in the charged state even if the battery is removed. Since the charges on the opposing plates are attracted through one another, they will tend to oppose any changes in charge. Within this manner, a capacitor will oppose any modification in voltage felt across it.
Electrons will find a path back to Plate A if we place a conductor across the plates, and the charges will be neutralized again. This is now a "discharged" capacitor that was show in the Figure.
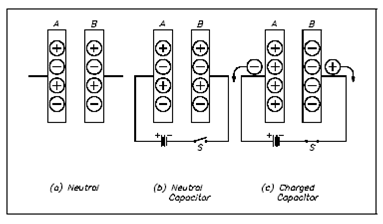
Figure: Discharging a Capacitor