Graphical Understanding of Derivatives:
A function expresses a relationship among two or more variables. For instance, the distance traveled through a moving body is a function of the body's velocity and the elapsed time. Whenever a functional relationship is presented in graphical form, an significant understanding of the meaning of derivatives can be developed.
Figure is a graph of the distance traveled through an object as a function of the elapsed time. The functional relationship display is given by the subsequent equation:
s = 40t
The instantaneous velocity v, that is the velocity at a given instant of time, equals the derivative of the distance traveled with respect to time, ds/dt. It is the rate of change of s with respect to t.
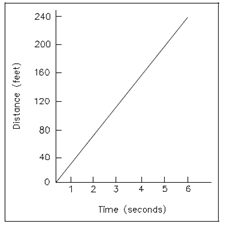
Figure: Graph of Distance vs. Time
The value of the derivative ds/dt for the case plotted in Figure can be understood by considering little changes in the two variables s and t.
Δs/Δt = (s+Δs) - s/(t +Δt) -t
The values of (s + Δs) and s in words of (t +t) and t, using Equation 4 can now be substituted within this expression. At time t, s = 40t; at time t + Δt, s +Δs = 40(t + Δt).
Δs/Δt = 40(t + Δt) - 40t/(t + Δt) - t
Δs/Δt = 40t +40(Δt) - 40t/t + Δt - t
Δs/Δt = 40(Δt)/Δt
Δs/Δt = 40