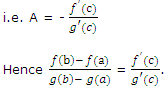Cauchy Mean Value Theorem:
Let ƒ and g be two functions classified on [a, b] such that
(i) g and ƒ are continuous in [a, b]
(ii) g and ƒ are derivable in ]a, b[
(iii) g'(x) ≠ 0 for each x ∈[a, b[ such
Then there exists at least one point c ∈]a, b[ so that
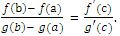
Proof: the shown hypothesis indicates that g(b) ≠ g(a) for if g(b) = g(a), then g takes the conditions of the Rolle's theorem and so ∃ some x0 ∈ [a, b[ such that g' (x0) = 0, which contradicts (iii).
let Ø (x) = ƒ(x) + A g (x) V x ∈[a, b]
where A is constant to be selected suitably. We get that
(i) Ø is continuous in [a, b] since g and ƒ are continuous in [a, b].
(ii) Ø is derivable in ]a, b[, since g and ƒ are derivable in ]a, b[.
Select the constant A such that Ø (a) = Ø (b)
i.e. ƒ(a) + A.g (a) = ƒ(b) + A.g (b)
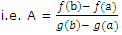
Since Ø satisfies all the required conditions of Rolle's theorem, there exists some c∈]a, b[ so that Ø'(c) = 0
i.e. ƒ'(c) + Ag'(c) = 0