pH
Being simultaneously acidic and basic, water goes through autoprotolysis, also termed as self-ionization:
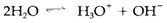
The equilibrium constant is
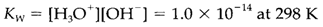
H3O+ in these equations is frequently just written H+. In pure water and in solutions which do not give any additional source of OH- or H+ both ions have molar concentrations equal to 10-7. Addition of an acid rises [H3O+] and hence get decreases [OH-]; addition of a base has the opposite effect. The pH scale is described by
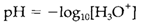
Neutral water has a pH of 7, acidic solutions have lower values (basically 0-7) and alkaline or basic solutions higher values (7-14). So, in alkaline solutions [OH-] is greater than [H+].