Pineal gland
The pineal gland is a circumventricular organ which secretes melatonin into the blood during the hours of darkness; the duration of the pineal melatonin pulse is a direct measure of the length of night and still also of day length, the photoperiod. The Melatonin secreted into the blood is transported across the blood–brain barrier to act on the SCN.
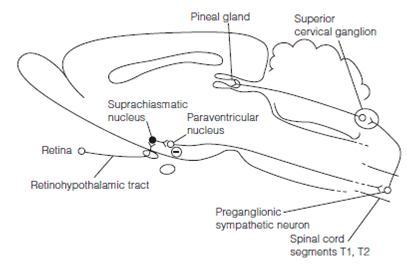
Figure: The brain circuitry by which light inhibits the secretion of melatonin from the pineal gland.
For animals living at latitudes other than the equator day length varies through the year, so melatonin secretion perform as a signal that codes for the time of the year. By seasonal breeders the length of the melatonin pulse regulates the hypothalamic– pituitary–gonadal (HPG) axis of both males and females through its action on the SCN. For instance, in sheep the longer melatonin signals produced in the shorter photoperiods of November (in the Northern hemisphere) activates estrous cycles in ewes and testicular growth—with a consequent rise in testosterone secretion and spermatogenesis—in rams. Although photoperiodic control of melatonin secretion is not important for reproduction in humans it does exert feedback effects on the function of the SCN circadian clock and so affects sleep–wake cycles.
The pathway through that light inhibits melatonin synthesis is circuitous in previous Figure. Neurons in the SCN which get retinal input from the RHT inhibit central autonomic neurons in the paraventricular nucleus (PVN). The PVN sends axons through the brainstem to synapse with preganglionic sympathetic neurons in the intermediolateral horn of spinal cord segments T1 and T2. This project to the superior cervical ganglion (SCG) the postganglionic cells of that innervate the pineal gland. At night the action of SCG neurons is increased and the secretion of noradrenaline from sympathetic terminals acts on β adrenoceptors of pinealocytes to synthesize melatonin. The biosynthetic pathway is described in above Figure.
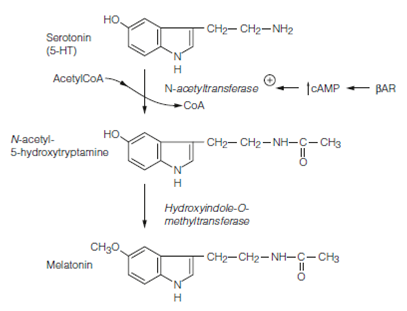
Figure: Synthesis of melatonin in the pineal. N-acetyl transferase is activated by norepinephrine, secreted from sympathetic terminals, acting at b adrenoceptors (bAR). cAMP, cyclic adenosine monophosphate.
In the SCN melatonin can carry the circadian clock, reset sleep–wake cycles in humans and animals, and reduce the symptoms of jet-lag, the sleep disturbance which arises when light–dark cycles and circadian rhythms are suddenly desynchronized through air travel over many time zones.