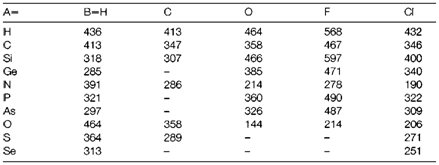
Major trends
A selection of single bond enthalpies is displayed in Table 1. Some significant trends are shortened below.
(i) Bond energies frequently become smaller on descending a main group (example C-H >Si-H>Ge-H). This is supposed as electrons in the overlap region of a bond are less strongly attracted to larger atoms. Some significant exceptions are noted in (v) and (vi) below, and the opposite trend is usually found in transition metal groups.
(ii) Bond energies get increases with bond order, even though the extent to which B(A=B) is larger than B(A-B) depends greatly on A and B, the largest differences occurring with elements from the set C, N, O. Strong multiple bonding involves these elements might be attributed to the very efficient overlap of 2pπ orbitals as compared with that of larger orbitals in lower periods.
(iii) In the compounds ABn with similar elements but distinct n values, B(A-B) decreases as n increases (example in the sequence ClF>ClF3>ClF5). The variations are usually less for the larger A, and more electronegative B.
(iv) Bonds are stronger among elements with a large electronegativity variations. This creates the basis for the Pauling electronegativity scale (see below).
(v) Single A-B bonds in which A and B are both from the set N, O, F are weaker than supposed from group comparisons. This is frequently attributed to a repulsion among nonbonding electrons, even though as in other cases of 'electron repulsion' the influence may be attributed to the Pauli exclusion principle more than to electrostatic repulsion.
(vi) Another exceptions to rule (i) above take place with A-O and A-X bonds (X being a halogen) that usually increase in strength between periods 2 and 3 (example C-O<Si-O). This may be partly because of the increased electronegativity variation when A is period 3, but repulsion among lone-pairs electrons on nonbonded atoms might also play a role (example F-F repulsion in CF4, in which the atoms are closer together than in SiF4).
Table 1. A selection of single-bond AB enthalpies (kJ mol-1)
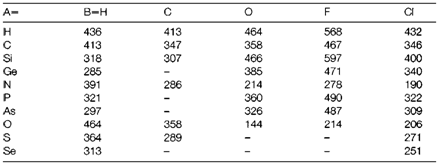
Table 2. Variation in bond enthalpy (kJ mol-1) with bond order