Film Boiling
Whenever the pressure of a system drops or the flow reduces, the bubbles can't escape as rapidly from the heat transfer surface. Similarly, when the temperature of the heat transfer surface is raised, more bubbles are formed. As the temperature continues to rise, more bubbles are formed than can be proficiently carried away. The bubbles grow up and group together, covering all small regions of the heat transfer surface with a film of steam. This is termed as partial film boiling. Because steam has a lesser convective heat transfer coefficient than water, the steam patch on the heat transfer surface performs to insulate the surface making heat transfer harder. Since the region of the heat transfer surface covered with steam rises, the temperature of the surface rises dramatically, whereas the heat flux from the surface reduces. This unstable condition continues until the affected surface is covered by a steady blanket of steam, preventing contact among the heat transfer surface and the liquid in the center of the flow channel. The situation after the stable steam blanket has formed is termed to as film boiling.
The procedure of going from nucleate boiling to film boiling is graphically symbolized in figure below. The figure shows the effect of boiling on the association among the heat flux and the temperature difference among the heat transfer surface and the fluid passing it.
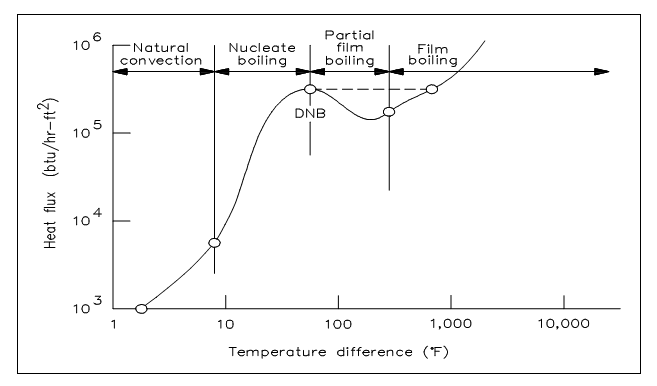
Figure: Boiling Heat Transfer Curve
Four regions are symbolized in the figure shown above. The first and second regions illustrate that as heat flux rises, the temperature difference (i.e., surface to fluid) does not change very much. Better heat transfer takes place during nucleate boiling than during natural convection. Since the heat flux rises, the bubbles become numerous sufficient that partial film boiling (portion of the surface being blanketed with bubbles) takes place. This region is characterized by a rise in temperature difference and reduces in heat flux. The rise in temperature difference therefore causes total film boiling, in which steam entirely blankets the heat transfer surface.