Modes of Operation of BJT
There are three forms of operation for BJT
1. Cut Off
Both the PN-junction of transistor is reverse -biased and the resultant mode of operation of the transistor in called as cut-off or just as off-mode. This means that the BJT will be "OFF" and no current will flow by it. The completely supply voltage will exist across it. In daily life an off switch will not allow any current to flow by an electric bulb and the full supply voltage will present across the switch.
2. Active Mode
This is when BEJ of a transistor is forward-biased and BCJ is reverse biased the mode of operation of a transistor is known as active-mode. A bipolar junction transistor in its active-mode of operation is known as an amplifier and is capable to intensify voltage or current signals both.
3. Saturation
If both the PN-junctions, i.e. the base-collector junction (BCJ) and the base-emitter junction (BEJ) are forward-biased, the transistor is referred to in its saturation (or ON) mode of operation.
EBJ CBJ
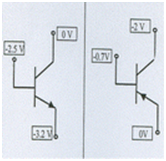
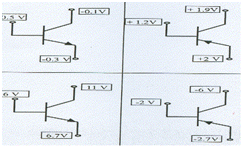
Cut Off Reverse Reverse
Active Forward Reverse
Saturation Forward Forward
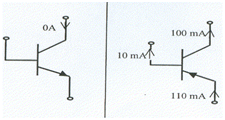
For the transistors given, give mode of operation.