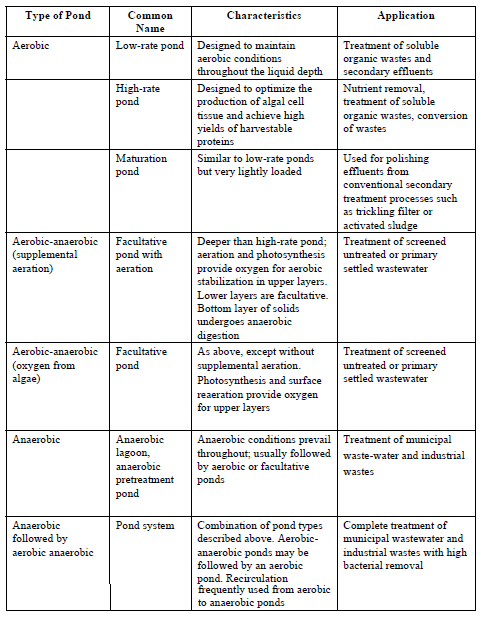
Stabilization Ponds
A stabilization pond is an associative shallow body of wastewater contained in an earthen basin, using a completely mixed biological process without solids return. Mixing may be either natural (wind, fermentation or heat) or induced (mechanical or diffused aeration). Stabilization ponds are commonly categorized on the basis of the nature of the biological activity in which takes place in them, as aerobic, anaerobic or aerobicanaerobic (Table 5). Aerobic ponds are used basically for the treatment of soluble organic wastes and effluents from wastewater treatment plants.
Aerobic-anaerobic (facultative) ponds are the most common type and have been used to treat domestic wastewater and a wide variety of industrial wastes. Anaerobic ponds, for their part those are particularly effectual in bringing about rapid stabilization of strong concentrations of organic wastes. Aerobic and facultative ponds are biologically complex. The bacterial population oxidizes organic matter, producing ammonia, carbon dioxide, sulphates, water and other end products, which are subsequently used by algae during daylight to produce oxygen.
Bacteria then use this supplemental oxygen and the oxygen provided by wind action to break down the remaining organic matter. Wastewater retention time ranges between 30 and 120 days. This is a treatment process that is very commonly found in rural areas because of its low construction and operating costs.
Table 5: Types and Applications of Stabilization Ponds