Light Microscopy
A beam of light is focused through a microscope using glass lenses to produce an enlarged image of the specimen In light microscopy. Microscope the specimen is illuminated from below with the beam of light being focused on to it by the condenser lens in a compound light. On to its focal plane the incident light that passes through the specimen is then focused by the objective lens, creating a magnified image.
Glass lenses are utilized to focus a beam of light on to the specimen under investigation in light microscopy. To produce a magnified image light passing through the specimen is then focused by other lenses.
Standard (brightfield) light microscopy is the most frequent microscopy technique which use today and uses a compound microscope. By a lamp in the base of the microscope The specimen is illuminated from underneath, on to the plane of the specimen with the light being focused by a condenser lens. By the objective lens Incident light coming through the specimen is picked up and focused on to its focal plane, creating a magnified image. By the eyepiece this image is further magnified, with the entirety magnification achieved being the sum of the magnifications of the individual lenses. For increase the resolution achieved by a compound microscope, the specimen is frequently overlaid
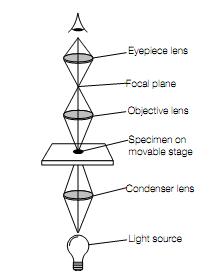
Optical pathway of a compound microscope.
with immersion oil into which the objective lens is placed. The restrication of resolution of the light microscope by using visible light is about 0.2 μm.