Transfer RNA:
Transfer RNA which is also known as tRNA is an adaptor molecule composed of RNA, classically 73 to 93 nucleotides in length, which serves as the physical link among the nucleotide sequence of nucleic acids and the amino acid series of proteins. It does this through carrying an amino acid to the protein synthetic machinery of a cell (ribosome) as directed through a three-nucleotide sequence (codon) in a messenger RNA that is mRNA. As like, tRNAs are a necessary parts of protein translation the biological synthesis of new proteins according to the genetic code.
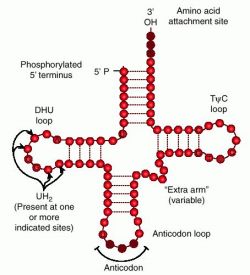
The exact nucleotide sequence of a mRNA specifies that amino acids are incorporated into the protein product of the gene from that the mRNA is transcribed and the role of tRNA is to specify that sequence from the genetic code corresponds to that amino acid. One end of the tRNA matches the genetic code in a three-nucleotide sequence known as the anticodon. The anticodon forms three base couples with a codon in mRNA in during protein biosynthesis. The mRNA instruct a protein as a series of contiguous codons every of that is identifies through a particular tRNA. Alternatively end of the tRNA is a covalent attachment to the amino acid which corresponds to the anticodon sequence.