Restrictions Enzymes:
A restriction enzyme or restriction endonuclease is an enzyme which cuts DNA at specific recognition nucleotide sequences with Type II restriction enzymes cutting double-stranded DNA called as restriction sites. Like enzymes, create in archaea and bacteria, are thought to have evolved to give a defense mechanism against occupy viruses. Within a bacterial host the restriction enzymes selectively cut up foreign DNA in a procedure known as restriction; host DNA is methylated through a modification enzyme (a methylase) to protect it from the restriction enzyme's activity. Cooperatively, these two procedures form the restriction modification system. For cut the DNA a restriction enzyme makes two incisions, once by every sugar-phosphate backbone of the DNA double helix.
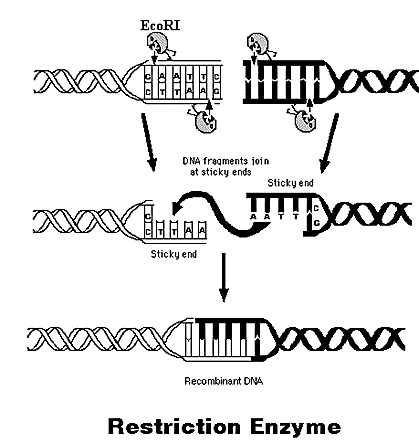
In order to be able to sequence DNA, it is first must to cut it into smaller fragments. Several DNA-digesting enzymes like those in your pancreatic fluid can do that but most of them are no use for sequence work since they cut each molecule randomly. This generates a heterogeneous set of fragments of varying sizes. What is required is a way to cleave the DNA molecule at a few precisely-located sites so which a small collection of homogeneous fragments are produced. The tools for these fragments are the restriction endonucleases. The rarer the site it recognizes the slighter the number of pieces generates through a given restriction endonuclease.