Protein sequencing and Peptide synthesis
Protein sequencing is a method to conclude the amino acid series of a protein, as well as that conformation the protein adopts and the extent to that it is complexed with any non-peptide molecules. Discovering the functions and structures of proteins in living organisms is a most important tool for understanding cellular processes and permits drugs which target specific metabolic pathways to be invented more simply.
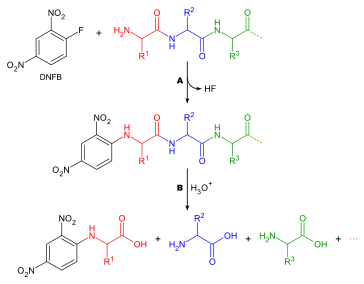
Peptide synthesis in organic chemistry is the production of peptides, that are organic compounds in that multiple amino acids are linked by amide bonds that are also known as peptide bonds. The biological procedure of producing long peptides (proteins) is known as protein biosynthesis. Peptides are synthesized through coupling the carboxyl group or C-terminus of one amino acid to the amino group or N-terminus of another. Due to the option of unintended reactions protecting groups are generally necessary. Chemical peptide synthesis starts at the C-terminal end of the peptide and ends at the N-terminus. This is another site of protein biosynthesis that begins at the N-terminal end.