Processing of Eukaryotic Pre-mRNA:
Unlike prokaryotes that have one RNA polymerase which builds all classes of RNA molecules and eukaryotic cells have three kind of RNA polymerase that are known as RNA pol I, RNA pol II and RNA pol III, and every kind of RNA is made through its own polymerase. Precursor mRNA (pre-mRNA) is an immature single strand of messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA). The Pre-mRNA is synthesized from a DNA template in the cell nucleus through transcription. The Pre-mRNA comprises bulk of heterogeneous nuclear RNA (hnRNA). The term hnRNA is frequently used as a synonym for pre-mRNA, while, in the strict sense, hnRNA should involve nuclear RNA transcripts which do not end up as cytoplasmic mRNA.
Overview
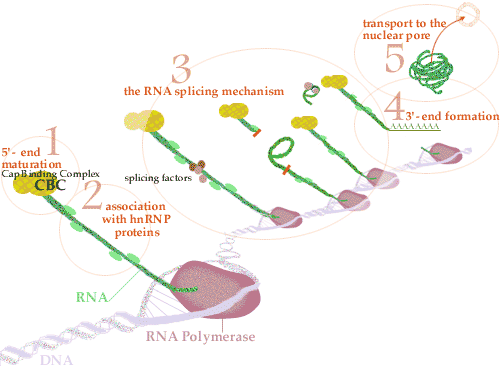
In the eukaryotes, the product of transcription of a protein-coding gene is pre-mRNA that needs to processing generate functional mRNA. Various processing reactions happen. Very soon after it has been synthesized through RNA polymerase II, the 5' end of the main RNA transcript, pre-mRNA is modified through the addition of a 5' cap a procedure known as capping. The primary RNA transcript which continues to be synthesized involves both noncoding (intron) and coding (exon) regions. The latter required to be erased and the exon sequences joined together through RNA splicing to generate a continuous RNA coding sequence ready for translation. RNA splicing reactions are catalyzed through a huge RNA-protein complex known as a spliceo- some which assembles on the primary RNA transcript as it is being synthesized so RNA splicing happen soon after RNA synthesis. At last the 3' ends of most but not all pre-mRNAs are modified through cleavage and the addition of about 200 A residues to form a poly (A) tail a procedure known as polyadenylation.
As defines earlier the C-terminal domain (CTD) of RNA polymerase II plays a role in transferring the 5' capping, RNA splicing and key polyadenylation parts to the growing RNA chain. Therefore transcription and RNA processing in eukaryotes are strongly coupled events.