Photosynthesis:
Photosynthesis is a procedure used by plants and other organisms to convert the light energy captured from the sun into chemical energy which can be used to fuel the organism's activities. The Photosynthesis occurs in algae, plants, and several species of bacteria but it will not occur in archaea. Photosynthetic organisms are known as photoautotrophs, because they can form their own food. In cyanobacteria, algae, and plants, photosynthesis uses carbon dioxide or water, releasing oxygen as a waste product. The Photosynthesis is vital for all aerobic life on Earth.
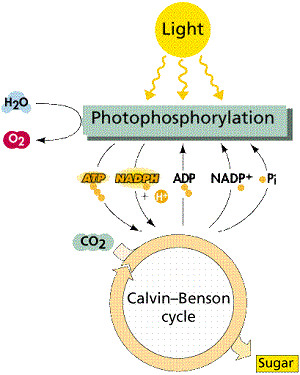
Additionally to maintaining normal stages of oxygen in the photosynthesis, atmosphere is the source of energy for closely all life on earth and either straightly, by primary production or not directly, as the ultimate source of the energy in their food, the exceptions being chemoautotrophs which live in rocks or around deep sea hydrothermal vents. The average rate of energy capture through photosynthesis globally is immense, approximately 130 terawatts, that is about six times larger than the power consumption of human civilization.