Pentose Phosphate Pathway:
The pentose phosphate pathway also known as the phosphogluconate pathway and the hexose monophosphate shunt is a procedure which produces pentoses 5-carbon sugars and NADPH. There are two distinct phases in the pathway. The first is the oxidative phase, in that NADPH is generated and the second is the non-oxidative synthesis of 5-carbon sugars. This pathway is an option to glycolysis. Although it does include oxidation of glucose, its major role is anabolic rather than catabolic. For most organisms, it will takes place in the cytosol and in plants, most steps take place in plastids.
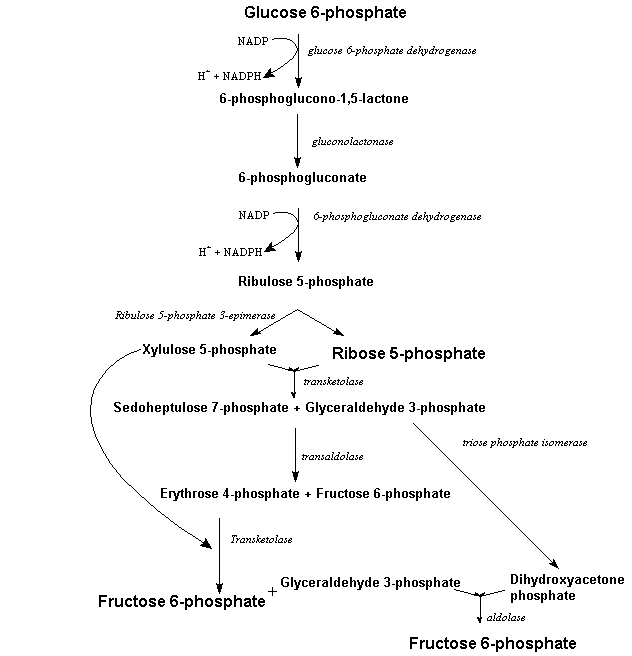
Reducing power is available in a cell both as NADPH and NADH but these have quite distinct roles. NADH is oxidized through the respiratory chain to produce ATP through oxidative phosphorylation. For biosynthetic reactions NADPH is used which reducing needs power. Despite their same structures, NADPH and NADH are not metabolically interchangeable and so the cell must carry out a group of reactions which specifically establish NADPH. This set of reactions is the pentose phosphate pathway also known as the hexose monophosphate shunt or the phosphogluconate pathway. It took place in the cytosol and is particularly important in tissues like as mammary gland, adipose tissue and the adrenal cortex which synthesizes fatty acids and steroids from acetyl CoA. The activity of the pathway is very low in skeletal muscle, for instance, that does not synthesize fatty acids or steroids.
The core group of reactions of the pathway oxidize glucose 6-phosphate to ribose 5-phosphate and generate NADPH. Therefore as well as producing NADPH the pathway has a 2nd very important role in converting hexoses into pentoses, in exacting ribose 5-phosphate. The Ribose 5-phosphate or derivatives of it are needs for the synthesis of NAD, RNA, DNA, ATP, flavine adenine dinucleotide FAD, CoA (coenzyme A) and other important molecules. Therefore the two major products of the pathway are ribose 5-phosphate and NADPH.