Operons:
In genetics an operon is a functioning unit of genomic DNA which is containing a cluster of genes under the control of a single regulatory promoter or signal. The genes are transcribed together into an mRNA strand and either translated both in the cytoplasm or undergo trans-splicing to establish monocistronic mRNAs which are translated separately; instance example is various strands of mRNA which each encode a single gene product. The conclusion of this is that the genes contained in the operon are may be expressed together or not at all. Various genes must be both co-transcribed and co-regulated to describe an operon.
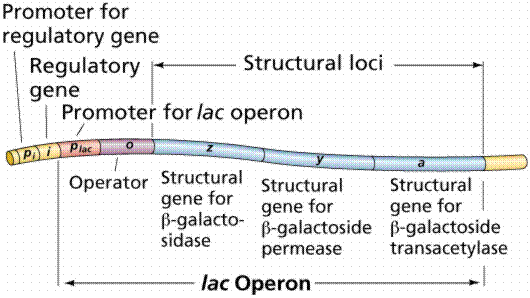
Initially, operons were thought to exist solely in prokaryotes but while the discovery of the first operons in eukaryotes in the early of the year 1990s, more evidence has arisen to suggest they are more general than previously assumed. Operons happen primarily in prokaryotes but also in some eukaryotes, involving nematodes like as C. elegans and the fly Drosophila melanogaster. rRNA genes frequently exist in operons which have been found in a range of eukaryotes involving chordates. An operon is made up of several structural genes arranged under a common promoter and regulated through a general operator. It is described as a group of adjacent structural genes plus the adjacent regulatory signals that affect transcription of the structural genes.