Myoglobin and hemoglobin
Hemoglobin is the iron-containing oxygen-transport metalloprotein in the red blood cells of all the vertebrates (having the exception of fish family Channichthyidae) as well as tissues of some invertebrates. Hemoglobin in blood carries oxygen from the respiratory organs to the rest of the body where it releases the oxygen to burn the nutrients to give energy to power the functions of the organism, and collects the consequential carbon dioxide to bring it back to respiratory organs to be dispensed from organism.
In mammals, protein makes up around 97 percent of the red blood cells' dry content, and around 35 percent of the total content. Hemoglobin posse’s oxygen binding capacity of 1.34 mL O2 per gm of hemoglobin that increases the total blood oxygen capacity 70-fold as compared to dissolved oxygen in blood. The mammalian hemoglobin molecule can carry up to 4 oxygen molecules.Hemoglobin is involved in transport of other gases: it carries the body's respiratory carbon dioxide (about 10 percent of the total) as carbaminohemoglobin, in which CO2 is bound to globin protein. The molecule carries the important regulatory molecule nitric oxide bound to globin protein thiol group, releasing it at same time as oxygen.
The partials of hemoglobin are also found outside red blood cells and their progenitor lines. Other cells which contain hemoglobin include the A9 dopaminergic neurons in substantia nigra, macrophages, mesangial cells and alveolar cells in the kidney. In these tissues, hemoglobin is having a non-oxygen-carrying function as an antioxidant and regulator of iron metabolism.
Hemoglobin and similar molecules are found in many fungi, invertebrates, and plants. In these organisms, hemoglobins can carry oxygen, or they can act to transport and regulate other things as nitric oxide, hydrogen sulfide, carbon dioxide, and sulfide. A variant of molecule, called as leghemoglobin, is taken in use to scavenge oxygen away from anaerobic systems, like the nitrogen fixing nodules of leguminous plants, before oxygen can poison the system.
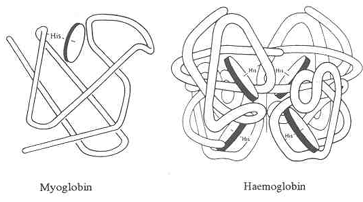
Myoglobin is a protein which binds iron- and oxygen found in the muscle tissue of vertebrates in general and in around all the mammals. It is related to hemoglobin that is the iron- and oxygen-binding protein in blood, particularly in the red blood cells. The time when myoglobin is found in the bloodstream is when it is released muscle injury. It is abnormal, and can be diagnostically relevant when found in the blood.It was the 1st protein which had 3-dimensional structure revealed. In the year 1958, John Kendrew and associates determined successfully the structure of myoglobin by high-resolution X-ray crystallography.