Membrane Proteins And Carbohydrate
The cell membrane is a slim semi-permeable membrane which surrounds the cytoplasm of a cell. Membrane function is to protect the integrity of the interior of the cell through allowing assured substances into the cell, although keeping other substances out. It also provides as a base of attachment for the cytoskeleton in some organisms and the cell wall in others. Therefore the cell membrane also serves to help support the cell and help preserve its shape. Plant cells, prokaryotic cells, fungal cells and Animal cells which have cell membranes.
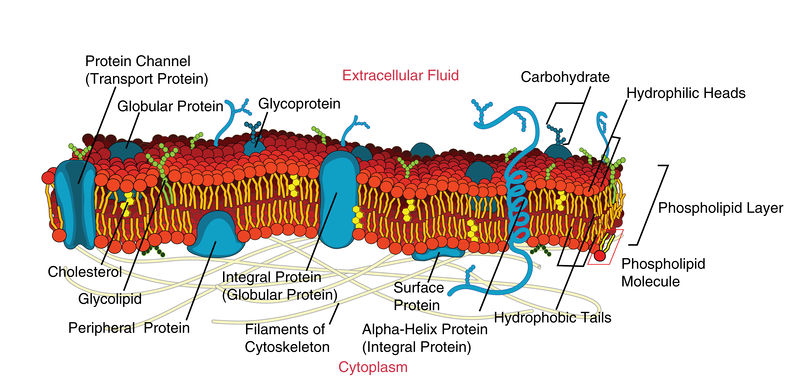
The Carbohydrate sets are covalently attached to several variant proteins to form glycoproteins. Carbohydrates are a much shorter percentage of the weight of glycoproteins than of proteoglycans. Various glycoproteins are elements of cell membranes, where they play a variety of roles in procedure like as cell adhesion and the binding of sperm to eggs. The carbohydrate is an organic compound which consists only of oxygen, hydrogen, and carbon commonly with a hydrogen oxygen atom ratio of 2:1 as in water; in other words with the empirical formula that is Cm H2O n. Some exceptions exist for instance deoxyribose is a component of DNA has the empirical formula C5H10O4. the Carbohydrates are not technically hydrates of carbon. It is more accurate structurally to view them as polyhydroxy ketones and aldehydes.