Lipoproteins:
A lipoprotein is a biochemical assembly which contains both lipids and proteins, bound to the proteins that permit fats to move by the water outside and inside cells. The proteins serve to soften the lipid otherwise known as fat molecules. Several enzymes, transporters, antigens, structural proteins, adhesins and lipoproteins are toxins. Instances involve the high-density and low-density lipoproteins, that enable fats to be carried in the blood stream, the transmembrane proteins of the chloroplast and the mitochondrion and bacterial lipoproteins.
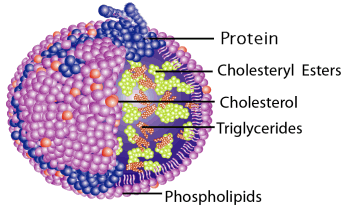
All cells use and rely on fats and for all animal cells, cholesterol as building blocks to establish the multiple membranes that cells use to both control inner water content internal water soluble elements and to organize their internal structure and protein enzymatic systems. The lipoprotein particle has hydrophilic sets of cholesterol, phospholipids and apoproteins directed outward. Like individuality make them soluble in the salt water-based blood pool. The cholesterol and Triglyceride-fats esters are carried inside, shielded from the water through the phospholipid monolayer and the apoproteins.