Introduction to Enzymes
Enzymes are huge biological molecules responsible for the thousands of chemical inter conversions which sustain life. They are greatly accelerating and highly selective catalysts both the specificity and rate of metabolic reactions from the digestion of food to the synthesis of DNA. Most enzymes are proteins, while some catalytic RNA molecules have been recognized. Enzymes adopt a specific three-dimensional structure and may employ organic like biotin and inorganic like magnesium ion cofactors to assist in catalysis.
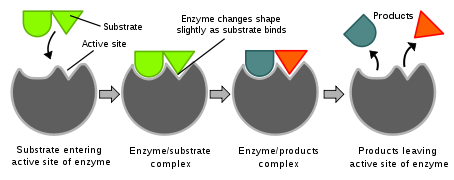
In enzymatic reactions the molecules at the starting of the procedure called substrates are converted into various molecules called products. Approximatly all chemical reactions in a biological cell require enzymes in order to occur at rates sufficient for life because enzymes are selective for their speed and substrates up only a few reactions from between several possibilities, the group of enzymes made in a cell determines that metabolic pathways occur in that cell.