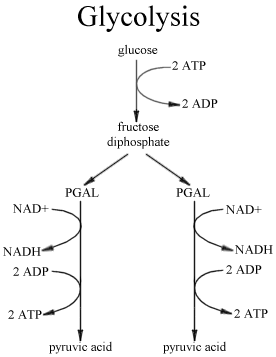
Glycolysis:
Glycolysis is a series of reactions shown in the figure which takes place in the cytoplasm of all eukaryotes and prokaryotes. The Glycolysis converts one molecule of glucose into two molecules of pyruvate that are then converted to acetyl coenzyme CoA (A) ready for entrance into the citric acid cycle. Two ATP molecules are needed for early reactions in the glycolytic way but four ATPs are generated later, providing a net yield of two ATPs per molecule of glucose degraded. Whole, glycolysis has a dual role. The first is to produce sATP. While only two ATPs per glucose are made straightly from the reactions of the glycolytic pathway, it also feeds substrates into the citric acid cycle and oxidative phosphorylation, where most ATP is build. The second role is to produce intermediates which act as precursors for a number of biosynthetic ways. Thus acetyl CoA, for instance, is the precursor for fatty acid synthesis.