Genetic Code:
The genetic code is the group of rules through that information encoded within genetic material DNA or mRNA sequences is translated into proteins (amino acid sequences) through living cells. The Biological decoding is accomplished through the ribosome that links amino acids in an order specified through mRNA, using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to hold amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. The genetic code is highly same between all organisms and can be expressed in an easy table with 64 entries.
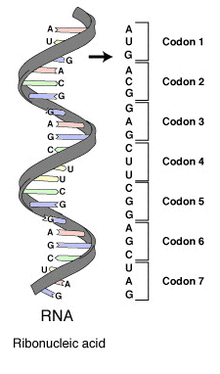
The code described how sequences of these nucleotide triplets, known as codons, specify that amino acid will be added next during protein synthesis. With some errors, a three-nucleotide codon in a nucleic acid series specifies a single amino acid. Since the vast majority of genes are encoded with specifically the similar code, this particular code is frequently referred to as the canonical or standard genetic code or easily the genetic code; by in fact some different codes have evolved. For instance, protein synthesis in human mitochondria relies on a genetic code which differs from the standard genetic code.