DNA Structure:
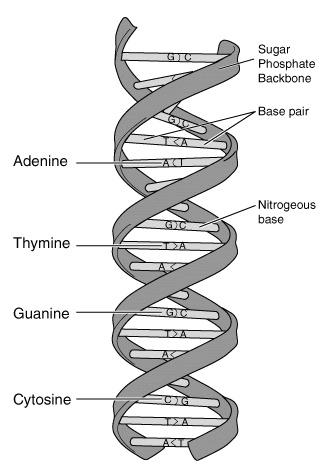
The Deoxyribonucleic acid or also known as DNA molecules are informational molecules encoding the genetic instructions used in the functioning and development of all known living organisms and several viruses. Beside with proteins and RNA, DNA is one of the three main macromolecules which are essential for all known forms of life. Genetic information is encoded as a series of adenine, nucleotides guanine, thymine, and cytosine recorded using the letters G, A, T and C. MAny DNA molecules are double-stranded helices consisting of two long polymers of simple units known as nucleotides, with backbones made of alternating sugars (deoxyribose) and phosphate collections, with the nucleobases attached to the sugars. The DNA is well-suited for biological information storage, because the DNA backbone is resistant to cleavage and the double-stranded structure gives the molecule with a built-in duplicate of the encoded information.
DNA exists in several possible conformations which involve A-DNA, B-DNA and Z-DNA forms, while, only B-DNA and Z-DNA have been straight observed in functional organisms. The conformation which DNA adopts depends on the hydration steps DNA sequence the amount and direction of supercoiling, chemical changes of the bases the kind and concentration of metal ions as well as the presence of polyamines in solution.