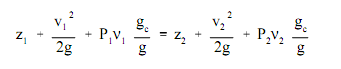Simplified Bernoulli Equation
Bernoulli's equation outcomes from the application of the general energy equation and the first law of thermodynamics to a stable flow system in which no work is completed on or by the fluid, no heat is transferred to and from the fluid, and no change takes place in the internal energy (that is, no temperature change) of the fluid. Under these situations, the general energy equation is simplified to the equation shown below.
(PE+KE+PV)1 = (PE+KE+PV)2
Replacing suitable expressions for the potential energy and kinetic energy, the above equation can be rewritten as follows:
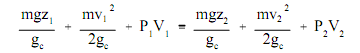
Here:
m = mass (lbm)
z = height above reference (ft)
v = average velocity (ft/sec)
g = acceleration due to gravity (32.17 ft/sec2)
gc = gravitational constant, (32.17 ft-lbm/lbf-sec2)
Note: The factor gc is only needed whenever the English System of measurement is employed and mass is measured in pound mass. It is necessarily a conversion factor required to permit the units to come out directly. No factor is essential when mass is measured in slugs or when the metric system of measurement is employed.
Each term in the above equation symbolizes a form of energy possessed by a moving fluid (kinetic, potential, and pressure associated energies). In spirit, the equation physically symbolizes a balance of the KE, PE, PV energies therefore when one form of energy rises, one or more of the others will reduce to compensate and vice-versa.
Multiplying all terms in the above equation by the factor gc/mg outcomes in the form of Bernoulli's equation shown by equation as follows: