Extended Bernoulli
The Bernoulli equation can be customized to take into account profits and losses of head. The resultant equation, termed to as the Extended Bernoulli equation, is very helpful in resolving most of the fluid flow problems. However, the Extended Bernoulli equation is probably employed more than any other fluid flow equation. The equation below is one form of the extended Bernoulli equation.
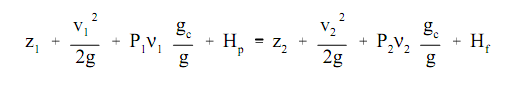
Here:
z = height above reference level (ft)
v = average velocity of fluid (ft/sec)
P = pressure of fluid (lbf/ft2)
ν = specific volume of fluid (ft3/lbm)
Hp = head added by pump (ft)
Hf = head loss due to fluid friction (ft)
g = acceleration due to gravity (ft/sec2)
The head loss due to fluid friction (Hf) symbolizes the energy employed in overcoming friction caused by the walls of the pipe. However it symbolizes a loss of energy from the standpoint of fluid flow, it does not generally symbolize a significant loss of total energy of the fluid. It also does not disobey the law of conservation of energy as the head loss due to friction outcomes in an equivalent rise in the internal energy (u) of the fluid. Such losses are maximum as the fluid flows via exits, entrances, pumps, fittings, valves, and any other piping with rough inner surfaces.
Most of the methods for computing head loss due to friction are empirical (depend almost completely on experimental evidence) and are depend on a proportionality constant termed as the friction factor (f).