Symbioses
Fungi can enter into close associations with other microbes and with higher plants and animals. These advantages are associated termed symbioses and in most cases the sym- biotic fungus gains carbohydrates from its associate while the associating organism gains nutrients and possibly protection from predation and herbivory or plant pathogens.
Fungal symbioses are common on plant roots, and the symbiotic roots are termed mycorrhizae. Their presence enhances nutrient uptake by plant roots and plant performance. The fungal association can be predominantly external to the root tissue. These associations are called ectomycorrhizae and can be seen on beech and pine trees, for example, and the fungal partners are members of the Dikarya. Other associations are predominantly within the plant root, and are termed endomycorrhizae. These associations are seen on the roots of herbaceous species like grasses, but are also found in the roots of tropical species of tree and shrub. These partnerships are with fungi in the Glomeromycota.
Other associations between fungi and plants can occur within leaves or stems, and these are called endophytic fungi. They live almost all their life cycle within the host, grow very slowly, and do not cause any signs of infection. They appear to protect their host from herbivory and fungal infection by the production of metabolites. However these products can have dramatic effects on herbivorous animals causing symptoms of fungal toxicosis similar to St Anthony’s fire.
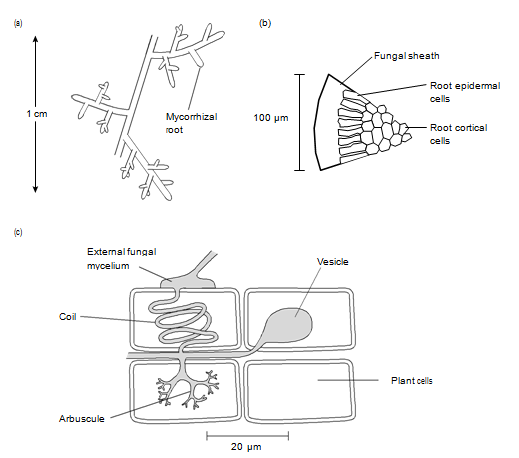
Figure 1. Structure of ectomycorrhiza and endomycorrhiza. (a) Macromorphology of ectomycorrhiza; (b) micromorphology of ectomycorrhizae; (c) micromorphology of endomycorrhizae. From Isaac S (1991) Fungal–plant interactions. With permission from Kluwer Academic.
Some fungi can form very intimate associations with algal species. These associations are termed lichens, and they have a form quite distinct from that of either component species, with crustose, foliose or fruticose thalli. They are slow-growing, and are adapted to occupy extreme or marginal environments such as bare rock faces walls and house roofs. As they are under quite extreme stress they are highly sensitive to pollution, for instance, from acid rain or heavy metals, and their presence or absence in an environment has become a useful indicator of urban and industrial pollution.
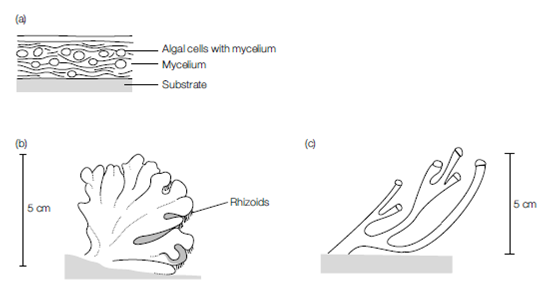
Figure 2. Lichen structure. (a) Crustose, tightly attached to substrate; (b) foliose, loosely attached to substrate; (c) fruticose, attached only at base.
Fungi can also associate with insect species in symbioses of varying intimacy. Some species of ants culture specific fungi on cut plant remains within their nests, and then browse on the fungal mycelium that develops. Termites have symbiotic fungi within their guts which–in association with a consortium of other microbes, including protista and bacteria – help the termite digest its woody gut contents.