Charging of Lead-Acid Battery:
As a lead-acid battery is charged in the reverse direction, the action declared within the discharge is reversed. The lead sulphate (PbSO4) is driven out and back into the electrolyte (H2SO4). A return of acid to the electrolyte will reduce the sulphate in the plates and increase the specific gravity. That will continue to happen until all of the acid is driven from the plates and back into the electrolyte, as display in Equation (4-2) and Figure.
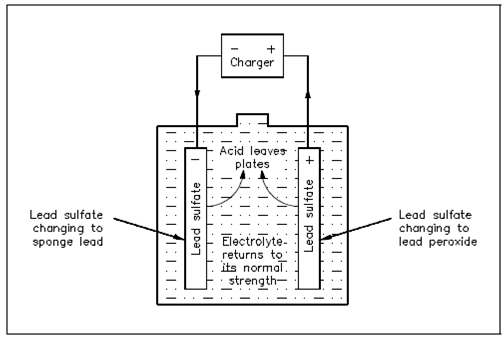
Figure 5 Chemical Actions during Charging
charge
PbO2 +Pb +2H2SO4 ← 2PbSO4 + 2H2O (4-2)
As a lead-acid battery charge nears finishing, hydrogen (H2) gas is liberated at the negative plate, and oxygen (O2) gas is liberated at the positive plate. That action occurs because the charging current is commonly greater than the current necessary to decrease the remaining amount of lead sulfate on the plates. The excess current ionizes the water (H2O) in the electrolyte. Because hydrogen is highly explosive, it is necessary to gives adequate ventilation to the battery whenever charging is in progress. Also, electric sparks, no smoking, or open flames are permitted near a charging battery.