Batteries:
The reason of a battery is to store chemical energy and to convert this chemical energy into electrical energy whenever the requirement arises.
As elaborate in earlier chapters, a chemical cell (or voltaic cell) consists of two electrodes of various types of metals or metallic compounds and an electrolyte solution that is capable of conducting an electric current.
A good instance of a voltaic cell is one which holds copper and zinc electrodes. The zinc electrode holds an abundance of negatively charged atoms, and the copper electrode holds an abundance of positively charged atoms. Whenever these electrodes are immersed in an electrolyte, chemical action starts. The zinc electrode will accumulate a much larger negative charge since it dissolves into the electrolyte. The atoms, which leave the zinc electrode that, are positively charged and are attracted through the negatively charged ions of the electrolyte; the atoms repel the positively charged ions of the electrolyte toward the copper electrode in the Figure.
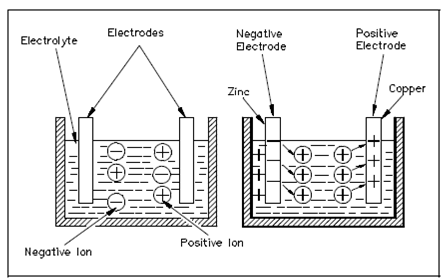
Figure Basic Chemical Production of Electrical Power
This action causes electrons to be erased from the copper electrode, leaving it along with an excess of positive charge. The forces of attraction and repulsion will cause the free electrons in the negative zinc electrode to move by the connecting wire and load if a load is connected across the electrodes, and toward the positive copper electrode that was show in the Figure.
The potential difference which results permits the cell to function as a source of applied voltage.
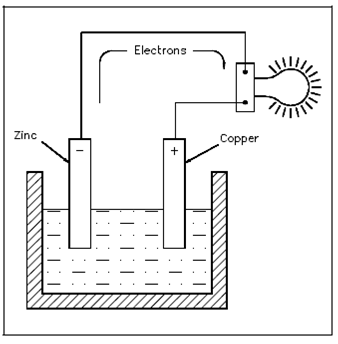
Figure Electron Flow Through a Battery